Cutting Edge Tech
- Sophie Byers
- Mar 27, 2024
- 4 min read
Information about laser machine's, the University of Regina's Makerspace, and more!

Last week I attended a laser cutter workshop and I decided to share what I learned. I would like to say that I am no expert and this is no way a conprehensive guide to using a laser and as a general rule it's always good to consult more than one source when learning a new skill. So without further ado enjoy!
Different types of laser cuts
A laser uses a highly concentrated beam of light to cut through materials. Lasers have three functions scoring, cutting, and engraving. Cutting is when the laser goes through the material completely making your project the specific size and shape required. The engraving setting lightly etches the material in question and scoring is basically just engraving at different depths.

An example of Scoring is the text underneath the photo. The photo and its contents like the tractor are engraved. And an example of cutting are the edges because the laser cut the photo down to the specific size needed.
CO2 vs Diode Lasers
There are two main types of lasers, CO2 and diode. CO2 lasers are much stronger and have a longer lifespan. Diode lasers are cheaper and more portable. Additionally CO2 lasers are good at using acrylic but requires special paste to cut through metal. There is a third type of laser machine called a laser engraver but the person running the workshop didn't mention it.
Suitable vs. Non-suitable materials
Suitable materials include
Wood: It depends what kind as not all work and if it is the right kind then beware of burn or charred marks on your project. Luckily playing with the settings and speed can reduce the risk. Usually 1/4 inch and 1/8 inch boards found in art stores are good but the ones from Home Depot or Lowe's are not.
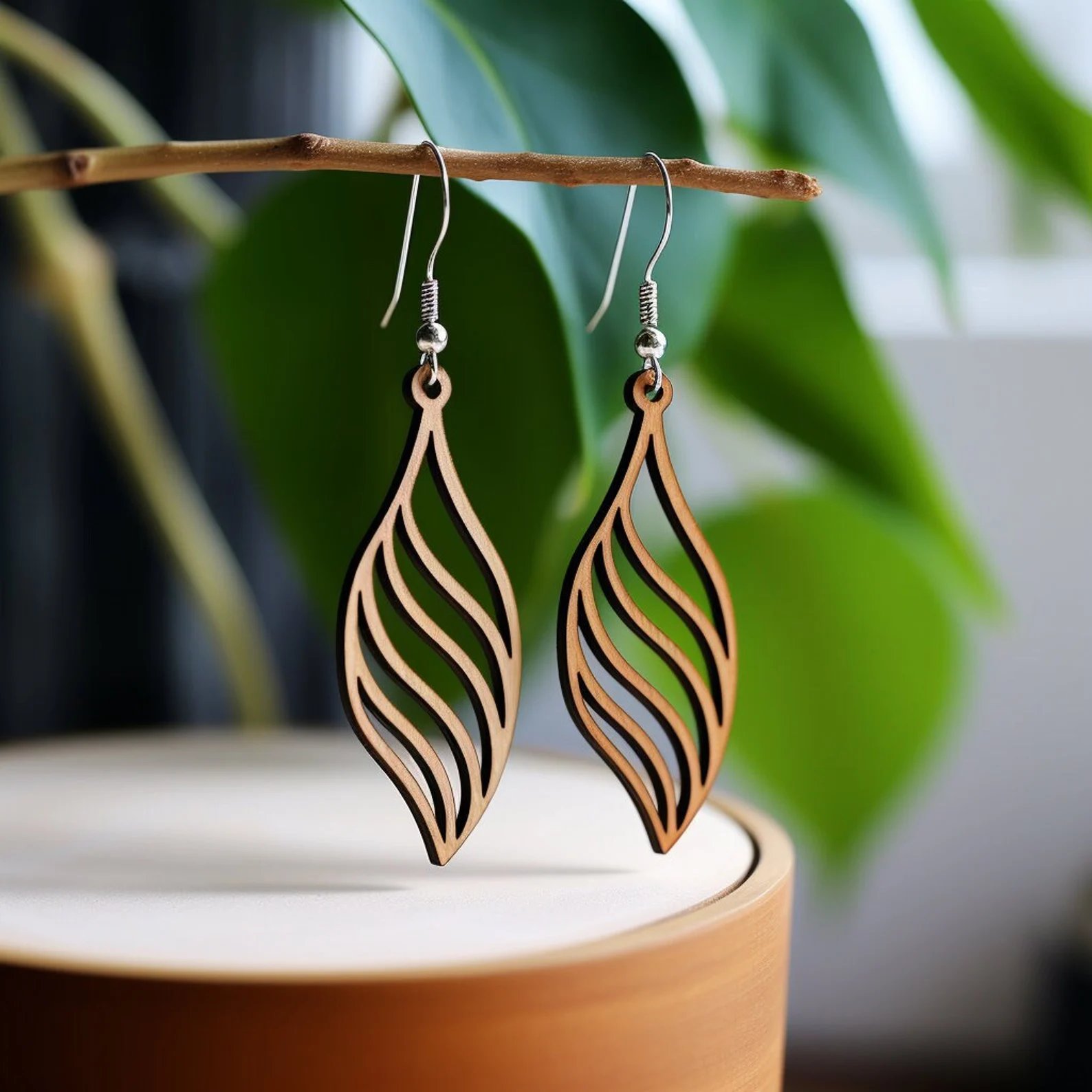
Plastic/Acrylic: This can make projects like the Mars light at the beginning of my post and comes out very beautifully when done right but not all variations of acrylic are safe to use. So just make sure it doesn't include any harmful elements that could be released into the air and that the laser is in a well ventilated space.
Metal: Engraving with this can be tricky but worth it when you see the final result.
Leather: This more complicated so I wouldn't recommend it if you're still a beginner and keep in mind that most leather doesn't work so make sure you get a specific kind.
Cardboard: One of the easiest and most inexpensive materials to work with.
Fabric: Apprently lasering fabric is a more recent option with faster results than embroidery. Cotton, nylon, polyester, and silk are good options.
Paper: As an alternative to cardboard, card stock paper can work for making some some models but it is mostly used to make custom cards.
Rubber: This isn't the most common materials but is great because it can be used for stamps, mats, keychains, and more.
Glass: This can be difficult to work with because of you're not careful the glass will crack but if done correctly will end up a beautiful frosted looked and is great for decorative items like coasters, vases, and cups.
Non suitable materials include
PVC(Polyvinyl Chloride): Chloride is not only corrosive but toxic to humans so it's not just a matter of hurting your machine it's hurting you tool
ABS(Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene): Releases cyanide a toxic gas that can lead to death if it is in a high enough concentration or in large quantities
Polycarbonate: This may not be as dangerous as some other materials mentioned but it is prone to catching fire and usually discolours when a laser comes into contact.
Polystyrene and Polypropylene Foam: These two materials run the risk of catching fire and if they don't they will just melt.
HDPE: This basically can't handle the heat and melts into a pile of goo. It can also catch fire.
Coated Carbon Fiber: This can result in developing a respiratory disease because of the toxic gases that are released.
Galvanized Metal: To prevent from rusting, galvanized metal is coated with zinc which when comes into contact with a laser releases the compound zinc oxide. This is extremely unsafe to people making galvanized metal incompatible with lasers.
Wood coated with a sealer or finish: I'm not actually sure why this isn't suitable but I'm guessing it has something to do the chemicals releases into the air when finished wood comes into contact with a laser.
In general plywood and acrylic are the materials are used the most but you should always check and make sure what materials are compatible with your laser machine .
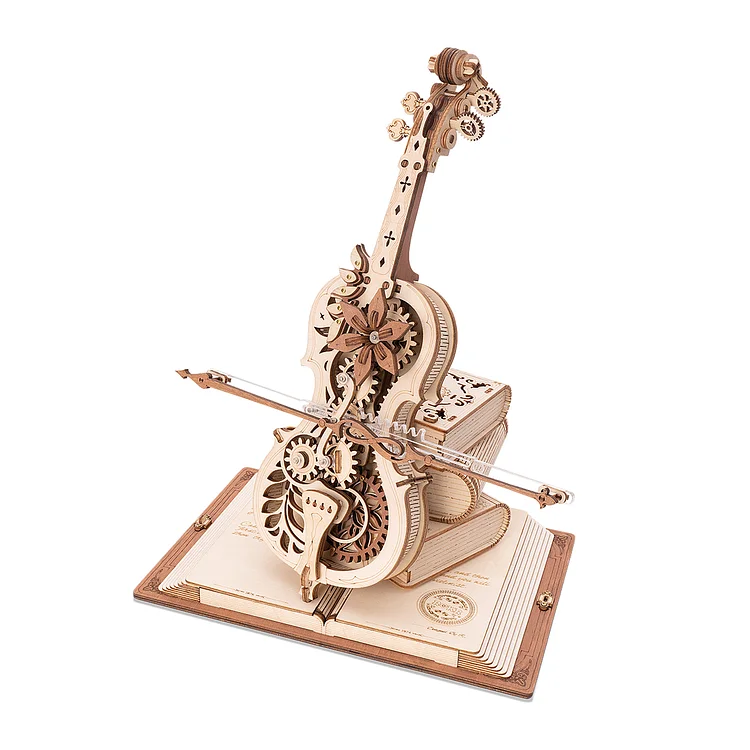
More project examples
Makerspace
For those of you don't know, the University of Regina's makerspace flooded last semester and is temporarily closed but is planning to be reopened by fall 2024. The makerspace is located in the basement of the Riddell Centre and is open twice a week. Students have to access to all the equipment including the Cricut, laser cutter, and more!
Closing Statement
In conclusion always check what is safe and if you are unsure just ask someone with more experience than you.
Sources
Fomitchev, George. “Diode Lasers vs. CO2 Laser Tubes. Advantages and Disadvantages.” EnduranceLasers, 30 Nov. 2021, endurancelasers.com/diode-lasers-vs-co2-laser-tubes/.
Li, Winnie. “Fiber Laser vs. CO2 Laser vs. Diode Laser: 3 Types of Laser Engravers and Cutters .” xTool, 7 Sept. 2023, www.xtool.com/blogs/buyer-guide/fiber-co2-diode-laser-difference.
Li, Winnie. “The Complete Laser Cutting Materials List.” xTool, 24 Feb. 2024, www.xtool.com/blogs/xtool-academy/laser-cutting-materials-list.











Comments